The term What is B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 Model is increasingly referenced in discussions around advanced analytical systems, adaptive decision frameworks, and next-generation optimization models. While the name itself appears highly technical, it reflects a layered and modular approach to handling complex data-driven processes rather than a single rigid algorithm.
At its core, the What is B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 Model represents a multi-stage computational and decision-optimization framework designed to integrate large datasets, apply structured processing logic, and deliver predictive or prescriptive outputs. The model’s design philosophy emphasizes scalability, adaptability, and iterative refinement, making it suitable for environments where data conditions change frequently.
This article explains what the B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 model is, how it is structured, how it functions, and why it is discussed in analytical and system-modeling contexts.
Understanding the Naming Structure of What is B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 Model
To understand the model, it is important to break down its naming convention, as each part indicates a functional layer or versioning logic.
The “B2K” Component
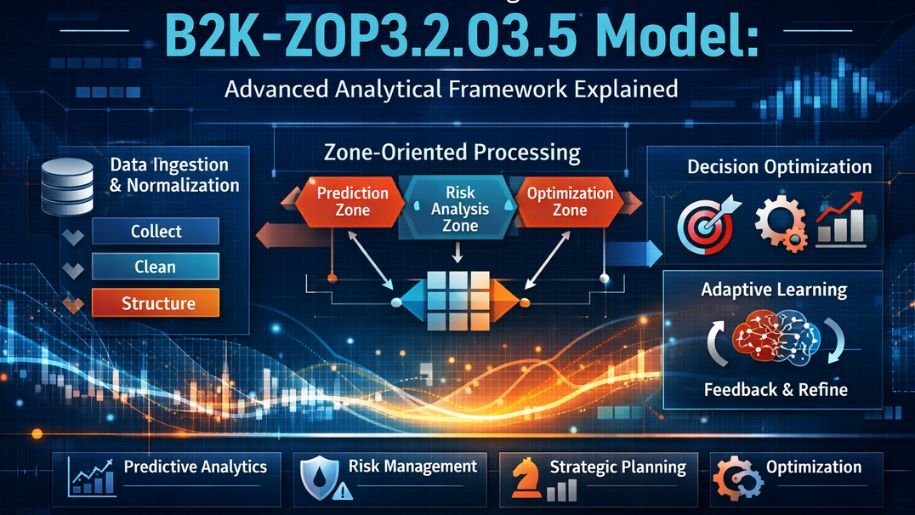
“B2K” typically denotes Base-to-Knowledge processing, a conceptual layer where raw data is transformed into structured, actionable knowledge. This stage focuses on ingestion, normalization, and contextual alignment of data from multiple sources.
In practical terms, the B2K layer is responsible for:
- Collecting data from heterogeneous systems
- Eliminating noise and redundancy
- Establishing baseline parameters for further analysis
This foundation ensures that higher-level computations operate on reliable and consistent inputs.
The “ZOP” Framework
“ZOP” refers to Zone-Oriented Processing, a modular approach where complex problems are divided into operational zones. Each zone handles a specific analytical or decision-making responsibility.
Rather than processing all variables in a single monolithic system, ZOP introduces separation of concerns. This allows:
- Independent optimization of each zone
- Parallel processing for efficiency
- Easier scaling and system updates
Version 3.2.03.5
The numerical suffix indicates iterative development maturity rather than a single static release. Each segment reflects refinements:
- Major version (3): architectural evolution
- Minor version (2): algorithmic improvements
- Patch and build identifiers (03.5): stability, tuning, and performance calibration
This suggests that the model is designed for continuous improvement rather than fixed deployment.
Conceptual Definition of the What is B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 Model
The B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 model can be defined as:
A layered analytical and optimization framework that transforms raw data into structured knowledge through zone-based processing, iterative refinement, and adaptive decision logic.
Unlike single-purpose algorithms, this model functions as a system architecture, allowing multiple analytical techniques to coexist within a unified workflow.
Core Architecture of the Model
Data Ingestion and Normalization Layer
The first operational stage focuses on acquiring data from diverse sources such as transactional systems, sensors, logs, or external feeds. This data is often inconsistent in format and quality.
The model addresses this by:
- Standardizing data schemas
- Handling missing or incomplete values
- Aligning timeframes and reference points
This step ensures downstream processes are not compromised by poor input quality.
Knowledge Structuring Layer
Once normalized, the data is transformed into structured representations. Patterns, relationships, and contextual markers are identified.
This layer often includes:
- Feature extraction
- Context tagging
- Semantic mapping
The outcome is a knowledge-ready dataset rather than raw numerical inputs.
Zone-Oriented Analytical Processing
Here, the ZOP concept becomes central. The system divides tasks into zones, each focused on a specific function such as prediction, risk evaluation, optimization, or trend detection.
Each zone:
- Operates semi-independently
- Uses specialized logic or algorithms
- Feeds results back into the central framework
This modular design reduces bottlenecks and enhances adaptability.
Decision Optimization Mechanism
A defining characteristic of the B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 model is its emphasis on optimization over static prediction.
Rather than simply forecasting outcomes, the model evaluates multiple decision paths and determines the most efficient or least-risk option based on defined constraints.
Key elements include:
- Objective functions that define success
- Constraint handling to respect real-world limits
- Iterative recalculation as new data arrives
This makes the model suitable for dynamic environments where decisions must be continuously refined.
Adaptive Learning and Feedback Loops
The model incorporates feedback mechanisms that allow it to learn from outcomes. Decisions made by the system are evaluated against actual results, and discrepancies are used to improve future performance.
This adaptive behavior includes:
- Error tracking and correction
- Parameter recalibration
- Zone-specific performance tuning
Over time, the system becomes more accurate and context-aware.
Practical Use Cases of the What is B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 Model
While the model itself is abstract, its structure lends itself to several real-world applications.
Predictive Analytics
The model can be used to anticipate trends by analyzing historical data patterns while adapting to new inputs in real time.
Strategic Planning Systems
Organizations can use the framework to simulate different scenarios and evaluate outcomes before committing to a decision.
Risk Assessment and Management
By isolating risk variables into dedicated zones, the system provides granular insights into potential vulnerabilities.
Operational Optimization
Processes involving logistics, resource allocation, or scheduling benefit from the model’s ability to evaluate multiple optimization paths simultaneously.
Strengths of the What is B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 Model
One of the model’s biggest advantages is flexibility. Its modular nature allows components to be updated without disrupting the entire system.
Other strengths include:
- Scalability across data sizes
- Improved transparency through zone separation
- Resilience against noisy or incomplete data
These characteristics make it suitable for complex and evolving environments.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its strengths, the model is not without challenges.
Implementation complexity is one concern, as designing effective zones and feedback loops requires deep domain knowledge. Additionally, performance depends heavily on the quality of data and the clarity of optimization objectives.
Without proper governance, the system may:
- Over-optimize narrow objectives
- Become computationally intensive
- Produce results that are difficult to interpret
Careful design and monitoring are essential.
How the Model Differs from Traditional Analytical Models
Traditional models often rely on linear workflows and static assumptions. In contrast, the B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 model emphasizes adaptability, modularity, and continuous refinement.
Instead of asking a single question and delivering a single answer, it supports ongoing decision evolution. This makes it better suited to modern, data-rich environments where conditions change rapidly.
Future Evolution of the Model
As computational capabilities improve, future iterations of the model are likely to focus on:
- Increased automation of zone configuration
- Enhanced explainability of decisions
- Better integration with real-time data streams
These advancements would further reduce manual intervention and improve trust in system outputs.
Why the What is B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 Model Matters
The growing interest in this model reflects a broader shift toward systems thinking in analytics and decision science. Organizations no longer rely on isolated algorithms; they require adaptable frameworks that can evolve with their data and objectives.
The B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 model embodies this shift by prioritizing structure, learning, and optimization over rigid computation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is the What is B2K-ZOP3.2.03.5 Model a single algorithm?
No. It is a framework composed of multiple layers and processing zones rather than a standalone algorithm.
Can the model be used with real-time data?
Yes. Its adaptive feedback loops and zone-based design make it suitable for real-time or near-real-time environments.
What industries benefit most from this model?
Industries that rely on complex decision-making, such as analytics-driven operations, planning systems, and risk management, benefit the most.
Is the model scalable?
The modular architecture allows it to scale horizontally by adding zones or vertically by increasing computational depth.
Does the model require machine learning?
Not necessarily. While it can incorporate machine learning techniques, it can also function using rule-based or statistical logic depending on implementation.